
- How to search in mac terminal how to#
- How to search in mac terminal mac os x#
- How to search in mac terminal mac#
Be cautious however because forcing a process to suddenly exit can have unforeseen consequences, so it’s advisable to check carefully that the process you are about to kill is the correct one. Once you know the process ID, killing it using Terminal is very simple. ps -ax | grep Skype yields the same result. Repeating the command with the Skype process ID instead i.e. The last line is just the process ID of the grep command itself, which can be safely ignored. This example shows that Skype has a PID of 14530 and also the folder where Skype was launched from. The “pipe” function (“|”) simply uses the output from the process list as an input to grep, to filter out the desired process name.Īssuming that Skype is actually running, you may see a result something like this:
How to search in mac terminal mac#
The process list displayed using ps -ax may include a hundred or more processes, but it’s quite simple to identify a process based on the name in the CMD column (for example Skype is listed as /Applications/Skype.app/Contents/MacOS/Skype), or even by the PID if you already know it.Īs shown in Activity Monitor earlier, the Mail application on my Mac had the PID 14649, so it’s simple to scroll down the Terminal window until the relevant process is found. Running Processes Displayed To Find a Specific Process

The simplest way to discover the available command-line options is to type the command into Terminal followed by -? such as ls -?Īnother useful command is apropos. Note that many commands in Terminal can accept various options (sometimes called switches) that can alter their effect.
How to search in mac terminal how to#
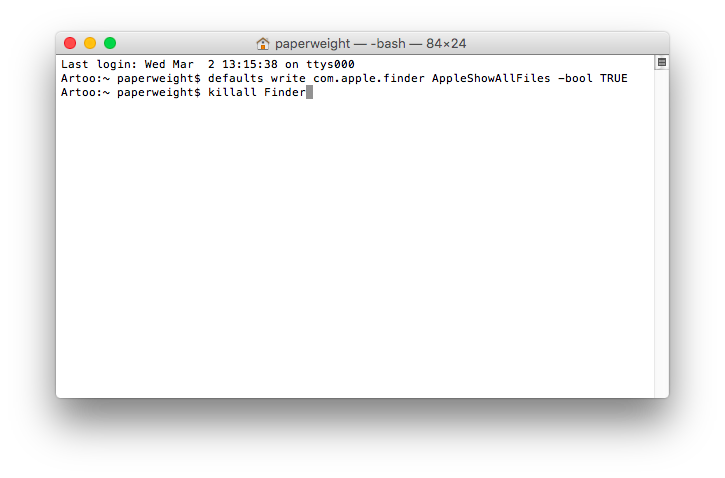
The current directory (the “working directory”) when you open Terminal always defaults to your Home Folder.īefore we describe how to check and terminate a process on your computer it’s worth knowing a few basic Terminal commands. The command prompt always begins with your computer name followed by your local Account Name. The second line is the command prompt which is where you enter the commands you wish to execute. The first line shows the date and time when you last logged in. Once it opens you’ll be presented with a standard Terminal window as below. Terminal is always represented by the icon below. The first step is to open Terminal either from the Applications -> Utilities folder or simply type Terminal into Spotlight. The Activity Monitor Application How to Use Terminal Note that process ID’s are assigned by Mac OS, and therefore will not be the same on your computer as somebody else’s. The Apple Mail application is displayed in Activity Monitor with a PID number of 14649. From here you can inspect or quit each process, but in this example we use Activity Monitor simply as a companion to Terminal. The main Activity Monitor window is shown below.Įach application on your Mac has an associated Process ID (a PID) and a user-friendly name.
When used together, Activity Monitor and Terminal provide a powerful yet relatively straightforward way to inspect and manage wayward processes. Activity Monitor shows common process-related details such as the memory used and percentage of CPU that each process is consuming. Terminal is a text-based tool which lets you conduct all manner of routine tasks such as viewing directories, copying, moving and deleting files, as well as obtain detailed information about each process running including:Ī related indispensable application is Activity Monitor – a graphical tool that allows you to manage processes, however it doesn’t have quite the same capabilities that Terminal does.

How to search in mac terminal mac os x#
Probably the most useful tool to check and kill processes is called Terminal, which is an application that provides access to the lower levels of the Mac OS X operating system and files.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
